Cardiac Arrest vs Heart Attack
By:
Apex Hospitals
05-11-2023 5 Min Read

A heart attack and cardiac arrest are both critical medical emergencies that can be life-threatening. Recognizing their distinct symptoms and knowing the appropriate actions can make the difference between life and death.
Imagine if a medical professional informed you that your dear one had suffered a heart attack instead of a cardiac arrest. How would you react? Would it bring relief or heighten your concerns? Understanding the disparities between these terms is crucial, as medical jargon can often be bewildering, especially in critical situations.
A heart attack occurs due to issues within the body's circulatory system, obstructing blood flow to the heart. The primary cause of most heart attacks is coronary artery disease. Heart attack risk factors include age, lifestyle choices like diet and exercise, and other medical conditions. In India, heart attacks are widespread and frequently reported.
On the other hand, cardiac arrest is characterized by a malfunction in the heart's electrical system. Typically, it is triggered by arrhythmias that disrupt the heart's rhythm and electrical functions. A cardiac arrest transpires when the heart's rhythm comes to a halt.
What is the difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest?
A heart attack, often medically termed a myocardial infarction, occurs when there is a blockage or interruption in the normal blood flow to the heart. The absence of an adequate supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart can damage one of the body's most vital organs, potentially causing the heart muscle to deteriorate.
Conversely, a cardiac arrest, also referred to as sudden cardiac death, involves the cessation of heartbeats. The term "arrest" signifies a cessation or halt. In the context of cardiac arrest, the heart's rhythmic beating comes to a standstill, representing a highly grave medical condition. Cardiac arrest has the potential to result in near-instantaneous death or severe disability.
Comparing Symptoms of Heart Attacks and Cardiac Arrests
Heart attacks and cardiac arrests are both critical medical emergencies. Understanding the symptoms of each can be lifesaving. Visit the best cardiology hospital to get the finest treatment.
Heart Attack Symptoms
Heart attacks often commence with sudden chest pain, although they can also start gradually with mild, intermittent pain that persists for several hours. The symptoms of a heart attack may vary, and if you've had one heart attack, your symptoms might differ if you experience another.
These symptoms can also differ between males and females, but chest pain remains the most common indicator of a heart attack for both genders. However, women are somewhat more likely than men to experience additional symptoms, including shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, and back or jaw pain.
Cardiac Arrest Symptoms
Cardiac arrests can occur unexpectedly, even in individuals who were unaware of their heart condition. A person undergoing cardiac arrest may suddenly collapse, lose consciousness, and may stop breathing or struggle to breathe.
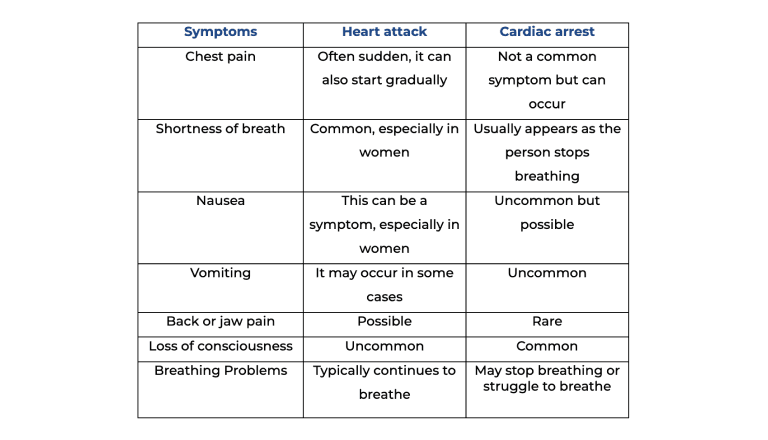
*Please note that these symptoms can vary from person to person, and not everyone will experience all of these symptoms during a heart attack or cardiac arrest. If you suspect someone is sharing these medical emergencies, seeking immediate medical help is crucial.
What are the causes and risk factors for a heart attack vs. cardiac arrest?
The causes and the risk factors for heart attacks and cardiac arrests are significantly distinct. Many individuals who experience a heart attack are aware of their risk factors. Conversely, cardiac arrests often occur unexpectedly in individuals who were unaware of any heart-related issues or risks.
Causes of Heart Attacks
Heart attacks are primarily caused by coronary heart disease, which restricts blood and oxygen supply to the heart. Most of the time, individuals are aware of their risk of a heart attack because they are being treated for heart disease.
Common risk factors for a heart attack may include:
- Unhealthy diet
- Lack of exercise
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- High blood pressure
- High blood sugar (diabetes)
- Being overweight
Causes of Cardiac Arrests
Several heart conditions and health factors can elevate the risk of cardiac arrest, including coronary heart disease. Other less predictable factors that can increase the risk of a cardiac arrest include:
- Enlarged heart
- Irregularly shaped heart valves
- Congenital (hereditary) heart conditions
- Electrical impulse abnormalities
- Smoking
- Family history of heart disease
- Previous heart attack
- Substance misuse
Understanding these causes and risk factors is vital for preventing and responding to heart attacks and cardiac arrests effectively.
How are heart attacks and cardiac arrests diagnosed?
A doctor can distinguish between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest through specific diagnostic procedures. This underscores the importance of seeking immediate medical attention if you suspect you or someone you know is experiencing either condition.
Diagnosis of a Heart Attack
To diagnose a heart attack, doctors conduct a physical examination and use an electrocardiogram to assess the heart's electrical activity.
Additionally, a doctor may order an echocardiogram or a cardiac catheterization to evaluate the heart's strength and function. Blood samples are commonly taken to detect indications of heart muscle damage.
Diagnosis of a Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest implies the heart has ceased to function, and without immediate resuscitation, it can be fatal.
If a doctor successfully restarts the heart and restores blood circulation, they will perform diagnostic tests to identify the cause of the cardiac arrest. These tests may involve an echocardiogram, blood tests, and a chest X-ray to detect any underlying heart-related issues or diseases.
What are the treatment options for a heart attack vs. cardiac arrest?
The choice of treatment for heart attacks and cardiac arrests depends on various factors, including:
- Medical Conditions and Medications: Your existing medical conditions and prescribed medications play a significant role in treatment decisions
- Severity: The seriousness of a heart attack or cardiac arrest is crucial.
- Overall Health: Your general health and ability to undergo surgical procedures or other treatments are considered.
Treating a Heart Attack
In the case of a heart attack, treatment varies based on the emergency's severity. The following procedures and treatments may be recommended:
- Stent placement
- Angioplasty
- Coronary artery bypass surgery
- Heart valve surgery
- Pacemaker implantation
- Heart transplant (in extreme cases)
Doctors often prescribe medications, including pain relievers, beta-blockers, and nitro-glycerine, to aid in recovery and reduce the risk of subsequent heart attacks.
Treating Cardiac Arrest
The primary treatment for cardiac arrest typically involves cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or defibrillation to restore heart function. After surviving a cardiac arrest, doctors may recommend various treatments to lower the risk of recurrence, including:
- Medications
- Surgical interventions
- Adoption of a healthier and more active lifestyle.
It's common to confuse the differences between a heart attack and a cardiac arrest, but the critical point to remember is that both are severe, life-threatening conditions.
If you suspect you or someone you know may be facing either of these conditions, seek medical assistance immediately. The medical experts and their team at Apex Hospitals can promptly evaluate your symptoms and initiate appropriate treatment. The speed at which you can reach a doctor or healthcare professional significantly impacts your recovery and prognosis.
Book your appointment now.
Related Articles
Connect with Us
Health in a Snap,
Just One App.
Know more




































































































