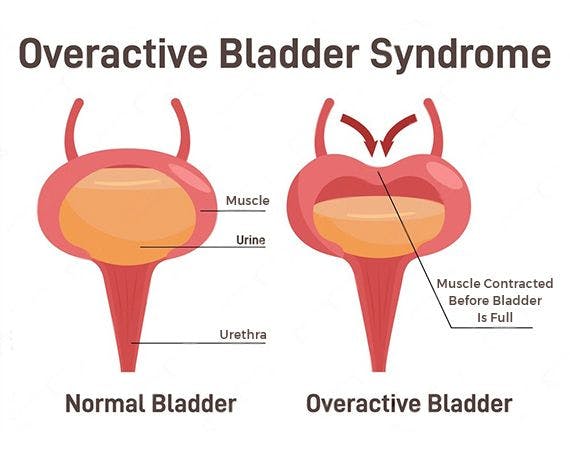
What is overactive bladder (OAB)?
Overactive bladder (OAB) refers to a cluster of urinary symptoms and is not classified as a disease. The predominant symptom is an abrupt and uncontrollable urge to urinate, often leading to involuntary urine leakage in some individuals. Another common manifestation is the frequent need to urinate throughout both day and night. OAB is characterized by a persistent sensation of needing to use the bathroom excessively.
How does an Overactive bladder (OAB) impact your life?
The impact of an Overactive Bladder (OAB) on your life can be substantial, affecting your work, social interactions, exercise routine, and sleep patterns. Untreated OAB symptoms can make daily activities challenging, necessitating frequent visits to the bathroom. Fear of being away from a restroom may lead to social withdrawal and feelings of isolation. OAB can strain relationships with friends and family, disrupt sleep, and impact one's sex life. The resulting lack of sleep can contribute to feelings of fatigue and discouragement. Additionally, if urine leakage occurs, it may lead to skin problems or infections. However, OAB can be effectively managed, and seeking advice from your healthcare provider is crucial if you suspect you have OAB.
Treatment for Overactive bladder (OAB)
Managing Overactive Bladder (OAB) involves exploring various strategies, and individuals may find that a combination of treatments works best for them. Collaborating with your healthcare provider is essential to determine your preferences and goals. OAB treatment options encompass:
1. Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle modifications, also known as behavioural therapy, may include altering dietary habits, adjusting fluid intake, and planning restroom visits strategically. These changes can significantly benefit many individuals.
- Limiting bladder-irritating foods and drinks: Avoid diuretics like caffeine and alcohol and identify specific foods that worsen symptoms.
- Bladder diary: Keeping track of bathroom visits to identify patterns and potential triggers.
- Double voiding and delayed voiding: Techniques to ensure complete bladder emptying and gradually extending the time between bathroom visits.
- Timed urination: Establish a regular bathroom schedule to prevent urgent feelings and regain control.
- Kegel exercises: Strengthening pelvic floor muscles to enhance bladder control.
- Quick flicks and biofeedback: Techniques involving rapid pelvic muscle contractions and using computer feedback to monitor muscle movement.
2. Medical and Surgical Treatments:
- Prescription Drugs: If lifestyle changes prove insufficient, medications, such as anti-muscarinic and beta-3 agonists, may be prescribed to relax the bladder muscle, reducing involuntary contractions. Various formulations, including pills, gels, or patches, exist.
- Bladder Botox Treatment: In cases where lifestyle changes and medications don't yield results, healthcare providers may administer Botox injections to relax the bladder muscle and alleviate urgency and incontinence. This treatment is typically performed in the office using a cystoscope.
- Nerve Stimulation: Neuromodulation therapy sends electrical pulses to nerves linked to the bladder's functioning. This helps correct the communication issues between the bladder and the brain, improving bladder function and alleviating OAB symptoms.
3. Surgery: In rare instances where other treatments are ineffective, surgical interventions may be considered. There are two surgical procedures available for specific cases. Augmentation cystoplasty involves enlarging the bladder, while urinary diversion reroutes the flow of urine. These surgeries are considered a last resort, offered only when no other viable options can provide relief, as they come with inherent risks and complexities. The decision to pursue such surgical interventions is made carefully, taking into account individual circumstances and the necessity for an effective and tailored approach.
Speak to our experts about overactive bladder
Are you experiencing frequent urges to urinate or sudden bladder contractions? It could be a sign of an overactive bladder (OAB). Don't let OAB disrupt your life – our team of specialists is here to help.
At Apex Hospitals, our experienced urology and bladder health experts can provide personalized care and support tailored to your needs. Whether you're seeking advice, diagnosis, or treatment options, we're dedicated to helping you regain control and improve your quality of life.
Book your consultation today and take the first step towards managing your overactive bladder effectively. Don't suffer in silence – let us guide you towards a happier, healthier future."
FAQS
Health In A Snap, Just One App.
KNOW MORE
