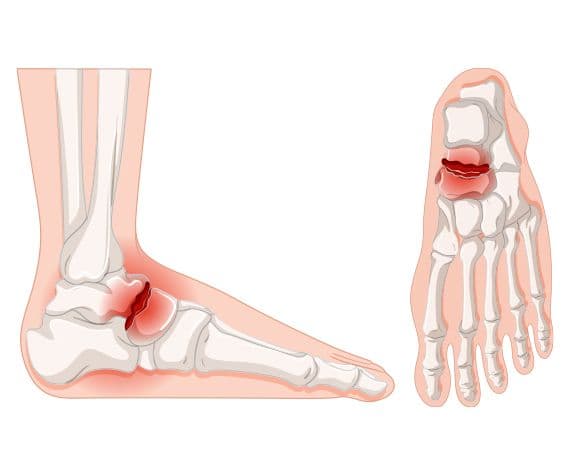
What is a fracture?
A bone fracture, commonly called a broken bone, occurs when there is a partial or complete break in the bone's structure. Fractures can affect any bone in the body and vary in severity. A closed fracture involves a break where the bone does not pierce the skin or damage surrounding tissue, while a compound fracture is more severe, as the broken bone penetrates the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
Fractures are often the result of trauma, such as falls, car accidents, or sports injuries. Still, they can also be caused by repetitive stress (like running) or underlying health conditions that weaken bones, such as osteoporosis.
What are the different types of fractures?
Fractures can be classified into various types based on their severity, pattern, and the way the bone breaks. Here are the different types of fractures:
1. Closed (Simple) Fracture:
The bone breaks but does not penetrate the skin.
2. Open (Compound) Fracture:
The bone breaks and pierces through the skin, increasing the risk of infection.
3. Transverse Fracture:
The break occurs in a straight line across the bone.
4. Oblique Fracture:
The break occurs at an angle across the bone.
5. Spiral Fracture:
The break twists around the bone, often caused by a rotating force or twisting injury.
6. Comminuted Fracture:
The bone shatters into three or more pieces, often requiring surgery.
7. Segmental Fracture:
The bone breaks in two places, leaving a floating segment between the breaks.
8. Greenstick Fracture:
A partial fracture is where the bone bends and cracks but doesn't break completely. Common in children due to softer bones.
9. Hairline Fracture:
A small crack in the bone, often caused by repetitive stress or overuse, is common in athletes.
10. Compression Fracture:
The bone is crushed, often seen in vertebrae due to osteoporosis.
11. Avulsion Fracture:
A tendon or ligament pulls away a fragment of bone due to sudden force.
How is a fracture treated?
The primary objective of fracture treatment is to realign the broken bone, alleviate pain, promote proper healing, prevent complications, and restore normal function to the affected area.
Treatment Options for Bone Fractures:
1. Immobilization (Splint or Cast)
A splint or cast is commonly used to keep the bone stable and prevent movement during healing. Splints are often used for less severe fractures and may be worn for three to five weeks, while casts, used for more complex fractures, may remain for six to eight weeks.
2. Medication
Pain management is essential during the healing process. Doctors may prescribe pain relievers to manage discomfort after a fracture.
3. Closed Reduction (Non-Surgical Realignment)
A closed reduction may be performed for more significant fractures where bones shift out of place, but the skin remains intact. The healthcare provider manually realigns the bones without surgery. To minimize pain during the procedure, local anaesthesia, sedation, or general anaesthesia may be administered.
Surgical Treatment Options:
1. Internal Fixation Surgery
Internal fixation is used when the bones need to be surgically repositioned and stabilized using metal hardware.
- Rods: Inserted through the bone's centre for stabilization.
- Plates and Screws: Metal plates screwed into the bone for secure alignment.
- Pins and Wires: Used for smaller bone fragments, often alongside rods or plates.
Some of these devices remain permanently, while others might need removal after healing.
2. External Fixation Surgery
This technique involves placing screws or pins into the bone on both sides of the fracture and attaching them to an external brace for stabilization. External fixation is often a temporary measure before internal fixation surgery.
3. Arthroplasty (Joint Replacement)
A joint replacement may be required if a fracture affects a joint (e.g., shoulder, knee, elbow). The damaged joint is replaced with a metal, ceramic, or plastic prosthetic to restore movement and function.
Speak to our experts about fractures.
Speak to our experts at Apex Hospitals for professional guidance and personalized treatment plans for bone fractures. Our specialized team offers advanced care, from diagnosis and pain management to surgery and rehabilitation, ensuring optimal recovery and long-term bone health. Schedule your consultation today to receive expert advice tailored to your needs.
FAQS
Health In A Snap, Just One App.
KNOW MORE
