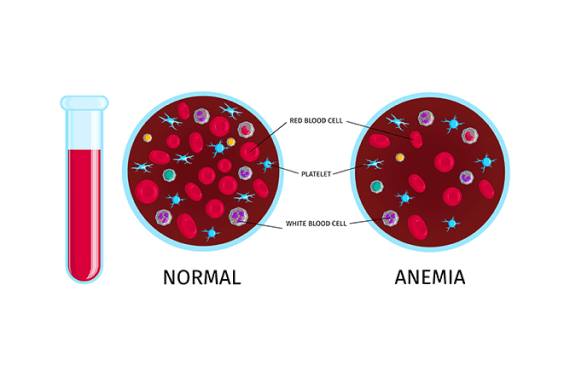
What is anemia?
Anemia arises from an insufficient count of healthy red blood cells or haemoglobin, hindering the efficient transport of oxygen to the body's tissues. Haemoglobin, a crucial protein housed within red cells, facilitates oxygen from the lungs to all organs. Common symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Various types of anemia exist, each with its unique underlying cause, spanning from transient to chronic conditions and varying severity. Anemia can serve as an indicator of underlying severe health conditions.
Treatment approaches for anemia may entail supplementation or medical interventions while maintaining a nutritious diet could prevent certain forms of anemia.
What are the diagnostic tests for anemia?
To ascertain the presence of anemia, your healthcare provider will likely conduct a comprehensive evaluation encompassing medical and family history inquiries, a physical examination, and requisition of blood tests. These tests may include:
Complete blood count (CBC): This test quantifies the various types of blood cells in a blood sample. For diagnosing anemia, the CBC assesses the levels of red blood cells, known as hematocrit, and the concentration of hemoglobin in the blood.
Typical hemoglobin values in adults typically range between 14 to 18 grams per deciliter for men and 12 to 16 grams per deciliter for women. Hematocrit values vary among medical facilities but usually fall within 40% to 52% for men and 35% to 47% for women.
A test to evaluate the morphology of red blood cells: This examination assesses the size, shape, and coloration, providing valuable insights into potential abnormalities.
What are the treatments for anemia?
A variety of treatments are available for anemia, all aiming to bolster the red blood cell count and enhance oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
The specific treatment modality depends on the type of anemia diagnosed. Common treatment approaches for prevalent forms of anemia encompass:
1. Iron-deficiency anemia: Addressed with iron supplements and dietary adjustments, with concurrent investigation and management of any underlying causes of excessive bleeding.
2. Vitamin deficiency anemia: Managed through dietary supplements and vitamin B12 injections.
3. Thalassemia: Treatment includes folic acid supplementation, iron chelation therapy, and, in certain cases, blood transfusions and bone marrow transplants.
4. Anemia stemming from chronic diseases: Management primarily focuses on addressing the underlying condition.
5. Aplastic anemia: Treatment typically involves blood transfusions or bone marrow transplants.
6. Sickle cell anemia: Managed with oxygen therapy, pain relief medications, intravenous fluids, and additional interventions such as antibiotics, folic acid supplements, blood transfusions, and the medication hydroxyurea.
7. Haemolytic anemia: Treatment strategies may encompass immunosuppressive medications, anti-infective therapies, and plasmapheresis—a procedure involving blood filtration.
Speak to our experts about anemia
If you're concerned about anemia or experiencing symptoms such as fatigue, weakness, or shortness of breath, don't hesitate to reach out to our team of experts for guidance and support. Our experienced healthcare professionals are here to help you understand your condition better and explore the most effective treatment options available.
Whether you're seeking a diagnosis, discussing treatment strategies, or simply looking for advice on managing your symptoms, our specialists are dedicated to providing personalized care tailored to your needs. We'll work closely with you to address any concerns you may have and develop a comprehensive plan to improve your overall health and well-being.
Don't let anemia hold you back from living your life to the fullest. Contact us today to schedule an appointment and take the first step towards better health.
FAQS
Health In A Snap, Just One App.
KNOW MORE
