Thrombocytopenia
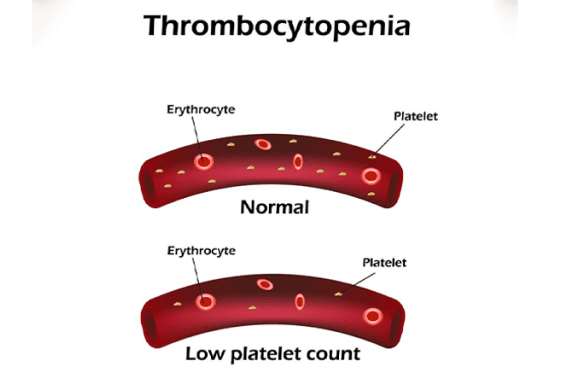
What is thrombocytopenia?
Thrombocytopenia is characterized by a low blood platelet count, which is crucial for clotting. Platelets, also known as thrombocytes, play a vital role in stopping bleeding by forming clots in blood vessel injuries.
This condition can arise due to various factors, including bone marrow disorders like leukaemia, immune system dysfunction, or as a side effect of certain medications. Thrombocytopenia can affect individuals of all ages, from children to adults.
While some cases of thrombocytopenia may present with mild symptoms or none at all, in rare instances, a significantly low platelet count can lead to severe internal bleeding, posing serious health risks. Fortunately, treatment options are available to manage thrombocytopenia and mitigate its effects.
How is thrombocytopenia diagnosed?
Healthcare professionals will conduct a comprehensive physical examination, observing for visible signs, such as bruises or rashes, that may indicate thrombocytopenia. They will inquire about your medical history, including a review of any medications you are currently taking. Additionally, diagnostic tests may be performed, including:
1. Complete blood count (CBC): This test assesses your blood's platelet, white blood cell, and red blood cell levels.
2. Peripheral blood smear: A microscopic examination of your platelets allows healthcare providers to assess their shape and quantity.
3. Blood clot test: These tests, such as partial thromboplastin time (PTT) and prothrombin time (PT), evaluate the time it takes to clot appropriately.
4. Bone marrow biopsy: In cases where blood tests indicate a low platelet count, a bone marrow biopsy may be conducted further to evaluate the bone marrow's production of platelets.
These diagnostic procedures aid healthcare providers in accurately diagnosing and determining the severity of thrombocytopenia.
Treatment
Treatment may not be necessary if a low platelet count is not causing significant complications. Often, healthcare providers focus on addressing the underlying cause to improve platelet counts. This approach may involve modifying medications.
Additionally, treatments may include:
1. Steroids: These medications can stimulate platelet production, potentially increasing platelet counts.
2. Blood transfusion: In cases of severely low platelet levels, healthcare providers may administer blood transfusions to raise platelet counts temporarily. However, the effects of transfusions typically last for about three days.
3. Splenectomy: Surgical removal of the spleen may be recommended if tests indicate that the spleen is sequestering a large number of platelets. It's important to note that individuals who undergo splenectomies have an elevated risk of developing infections. As a preventive measure, they may receive vaccinations to reduce this risk.
Speak to our experts about thrombocytopenia.
Are you experiencing symptoms of thrombocytopenia or have concerns about your platelet count? Our team of experts is here to help. Thrombocytopenia, characterized by a low blood platelet count, can pose various challenges and require proper management.
Our knowledgeable healthcare professionals can provide personalized guidance and support tailored to your needs. Whether you have questions about potential treatments, need assistance understanding your diagnosis, or want to explore preventive measures, we're here to address your concerns.
Don't let thrombocytopenia impact your quality of life. Speak to our experts today to receive the comprehensive care and information you need to manage your condition effectively. Your health and well-being are our top priorities.
FAQS
Health In A Snap, Just One App.
KNOW MORE
